Cable routing and bend radius
To maximize cable performance and lifespan, it’s important to ensure that all cables are routed correctly and adequate space is provided to allow for each cable’s minimum bend radius.
Minimum cable bend radius
CableBend radius
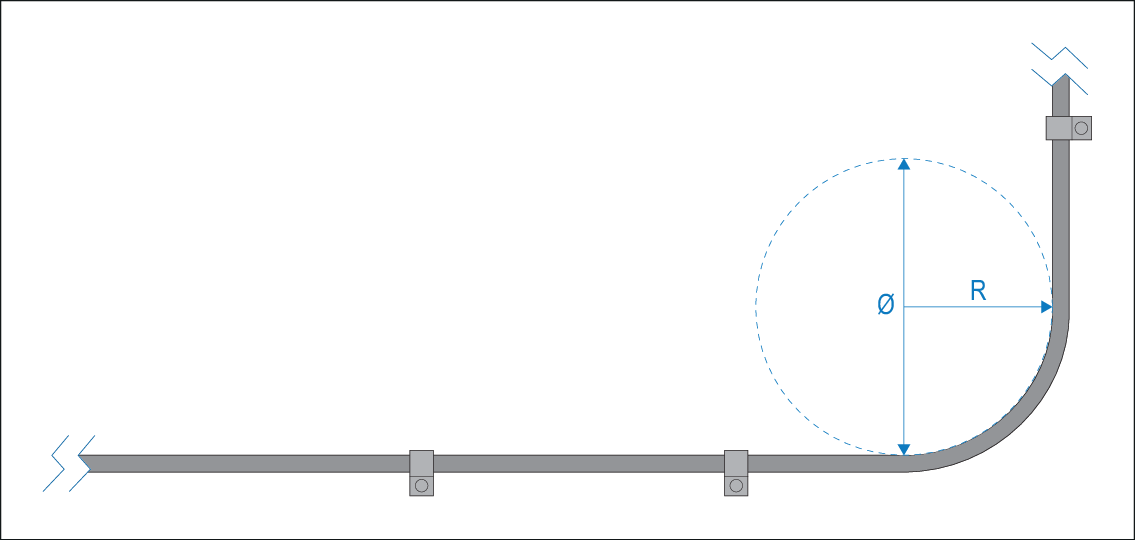
Do NOT bend cables excessively. Wherever possible, ensure that your chosen product installation location allows enough clearance for the minimum cable bend diameter specified in the following table:
| CableBend radius | Description |
Value |
|---|---|---|
Ø |
Cable minimum bend diameter. |
200 mm (7.87 in.) |
R |
Cable minimum bend radius. |
100 mm (3.94 in.) |
For products where multiple different cable types are connected, each with a different minimum cable bend radius, the higher figure is provided in the table above (i.e. the cable with the greatest minimum bend radius is specified).
Cable routing — best practices
CableRouting
CableProtectionProtect all cables from physical damage and exposure to heat. Use trunking or conduit where possible. Do NOT run cables through bilges or doorways, or close to moving or hot objects.
CableSecuritySecure cables in place using cable clips or cable ties. Coil any excess cable and tie it out of the way.
Where a cable passes through an exposed bulkhead or deckhead, use a suitable watertight feed-through (conduit).
Do NOT run cables near to engines or fluorescent lights.
Always route data cables as far away as possible from:
Other equipment and cables.
High current-carrying AC and DC power lines.
Antennas.